American workers are pessimistic about the employment outlook for 2026, with 49 percent expecting layoffs to be more common this year, according to a recent survey by résumé template service Zety. The survey results, published in Zety’s 2026 Job Predictions Report, highlighted the concerns of U.S. workers heading into the new year. In addition to […]
Already an Subcriber? Log in
Get Instant Access to This Article
Become a Central New York Business Journal subscriber and get immediate access to all of our subscriber-only content and much more.
- Critical Central New York business news and analysis updated daily.
- Immediate access to all subscriber-only content on our website.
- Get a year's worth of the Print Edition of The Central New York Business Journal.
- Special Feature Publications such as the Book of Lists and Revitalize Greater Binghamton, Mohawk Valley, and Syracuse Magazines
Click here to purchase a paywall bypass link for this article.
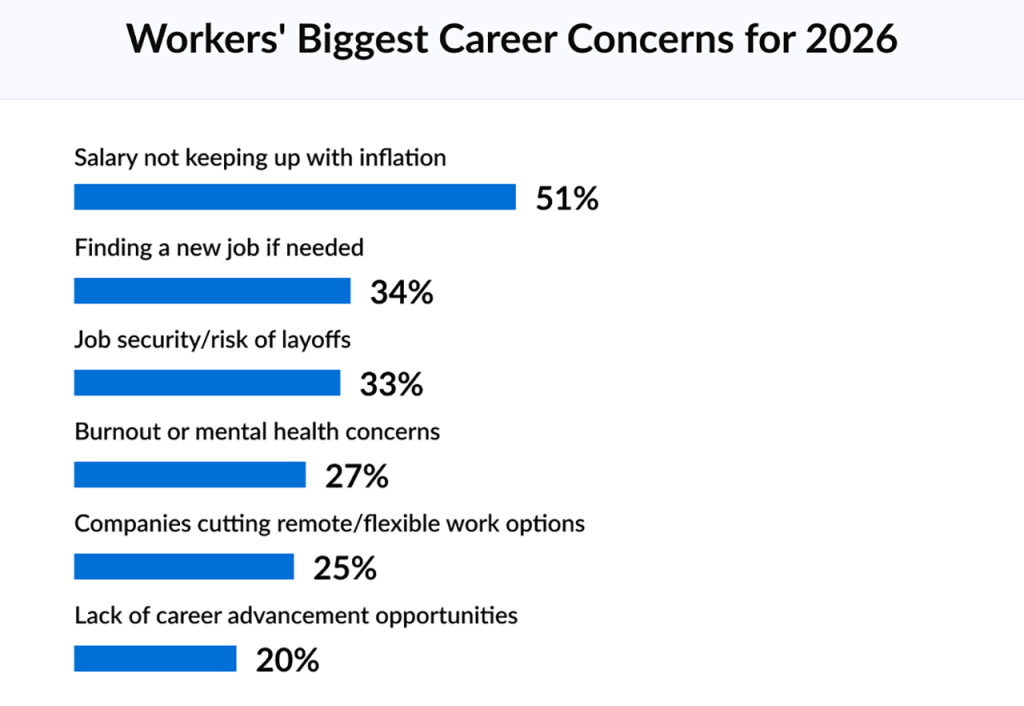
American workers are pessimistic about the employment outlook for 2026, with 49 percent expecting layoffs to be more common this year, according to a recent survey by résumé template service Zety.
The survey results, published in Zety’s 2026 Job Predictions Report, highlighted the concerns of U.S. workers heading into the new year. In addition to the widespread expectation for more layoffs, 65 percent of the respondents believe that the overall U.S. job market will be the same or weaker in 2026 compared to last year.
Some additional key findings from the study include the following:
• Over half (51 percent) of respondents say their top worry is their pay not keeping up with inflation.
• Almost one-third (30 percent) of workers expect remote work opportunities to decline in the face of corporate return-to-office initiatives.
• Competition from AI and automation is expected to be a barrier to getting hired by 48 percent of respondents.
• A majority (69 percent) of workers believe that having AI and tech skills will be of key importance in finding a job this year.
“With wage growth lagging behind inflation and job security top of mind, employees are entering 2026 facing more uncertainty than in recent years,” Jasmine Escalera, a career expert for Zety, said of the findings. “This is a moment for workers to think strategically about their careers, invest in skills that will keep them competitive, and focus on opportunities that offer both stability and growth potential.”
The survey was conducted by Zety, using the Pollfish survey platform, on Dec. 12, 2025. Responses were collected from 1,003 U.S. employees. The survey sample consisted of 48 percent female and 52 percent male, with 20 percent Gen Z, 26 percent Millennials, 27 percent Gen X, and 27 percent Baby Boomers.